Medical Triage Guidance System
Release time:
2023-09-14
With the continuous deepening of medical system reform, competition in the medical market has become increasingly fierce. In order to better enhance the hospital's image and improve core competitiveness, it is essential to utilize high-tech information methods to optimize the medical process. Ensuring that patients can seek medical care in an orderly and easy manner has become an urgent requirement for hospitals to improve their medical service levels. Under this demand, the intelligent guidance and information release system for hospitals has emerged.
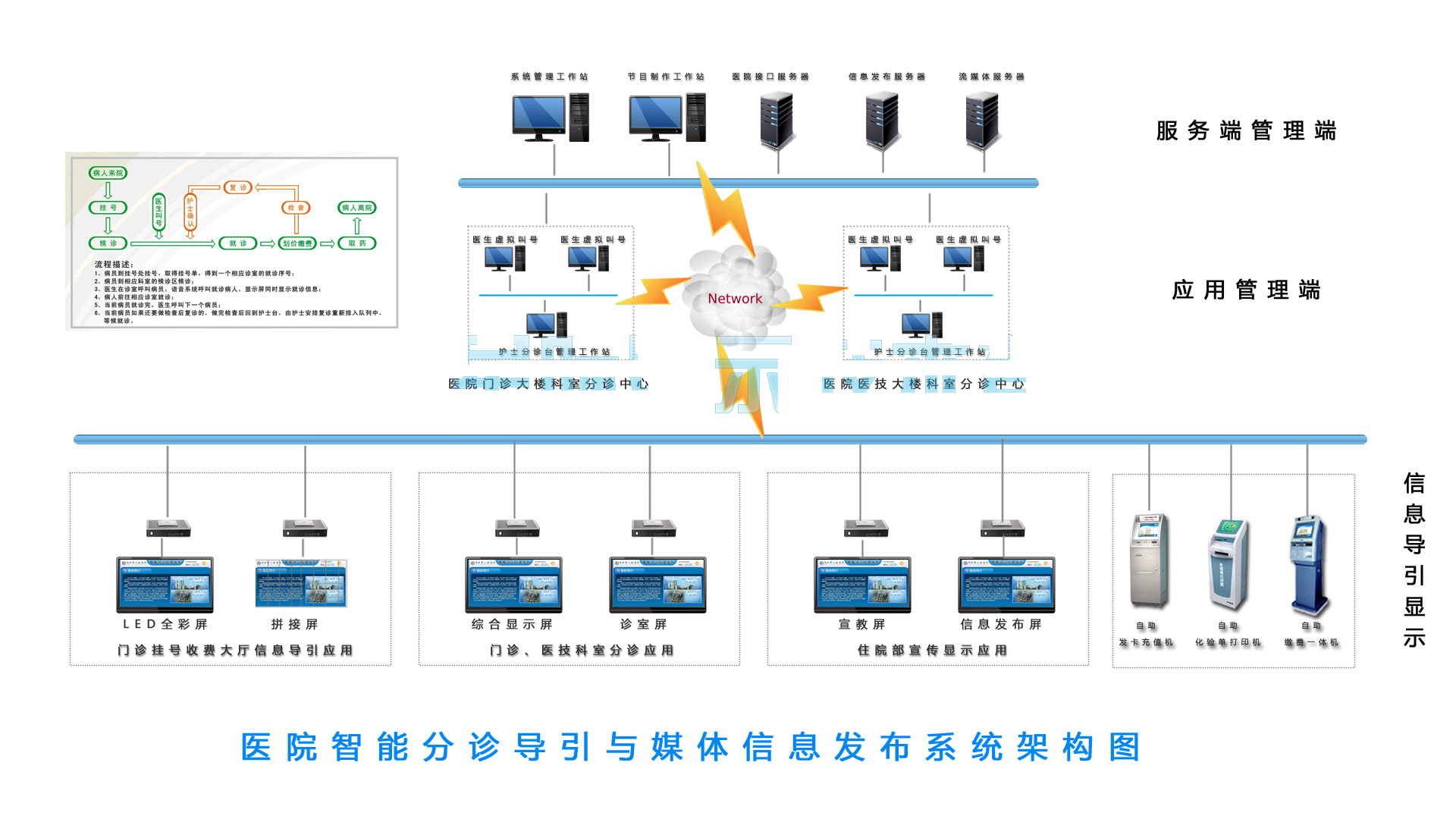
The system adopts a distributed structure with centralized and hierarchical management. It supports at least three levels of management: hospital, department, and clinic. The guidance information management center server remotely controls the terminal player through the network, achieving intelligent guidance and information transmission, control, and broadcasting. The central server manages the front-end display screens, touch query integrated machines, and LED displays in a unified manner, greatly reducing management costs and improving work efficiency.
The front-end display of the system uses a B/S architecture, which separates the management platform from the server. Users can log in to the server through the internet or the hospital's internal network to complete content design and publishing. Programs are transmitted over the network to each playback terminal for local playback. The call triage client adopts a C/S architecture to ensure real-time and accurate data.
(System Architecture Diagram)
- Network Platform: It can be the hospital's local area network. The system requires a bandwidth of: central exit 10Mbps, terminal node 1Mbps, and supports Wi-Fi wireless network. The switch in the diagram supports layer 2 switching.
- Information Publishing Server: The core of the system, it can use a high-performance PC architecture server, equipped with the main service program of the system, for multimedia content storage, scheduling, and database operation. It should have good bandwidth guarantees with the network.
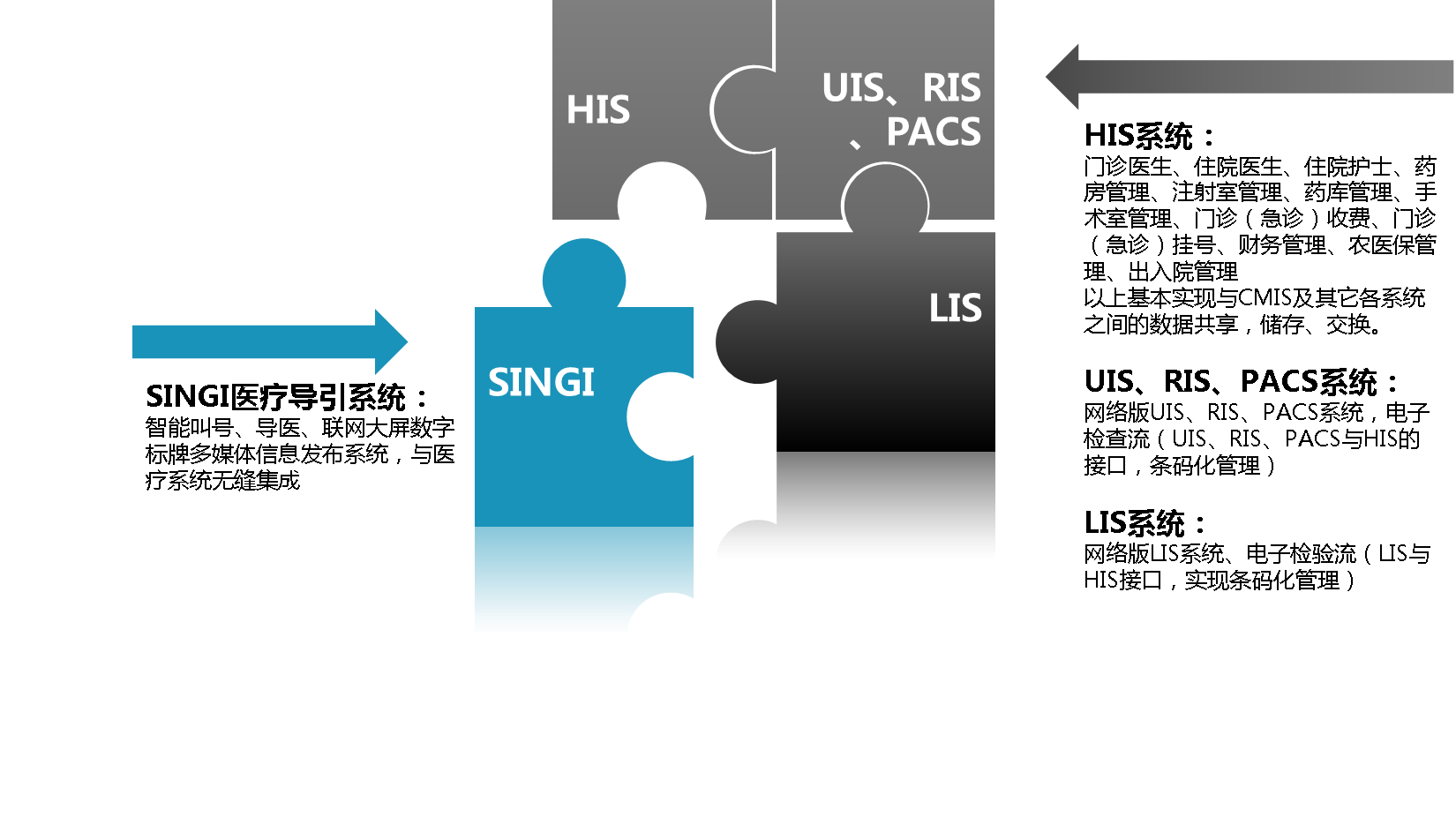
- Triage Server: Used to receive information from HIS interface servers, doctors' clinic computers, and nurse station computers, generating the latest triage guidance information in real-time and pushing it to various display terminals according to display rules. In smaller systems, it can be combined with the information publishing server into one.
- HISInterface Server: This is the interface machine that communicates with the existing HIS system in the hospital. It can be designed in a dual-network mode to ensure the security of the HIS system and can be combined with the information publishing server into one based on actual conditions.
- Management Workstation: Used for system management, including system settings, monitoring, content organization, publishing, and maintenance. Existing PC equipment in the hospital can be utilized, and multiple management workstations can be designed based on permissions.
- Doctor's Clinic Computer: Uses the hospital's existing computer, equipped with virtual call number software, making it convenient for doctors to call patients. Each doctor's clinic computer must install the "Virtual Call Number" software.
- Nurse Station Computer: Uses existing hospital equipment, equipped with "Shunhua Medical Guidance" triage software, allowing nurses to easily retrieve queue information, patient number adjustments, and other tasks.
- Media Playback Display Machine: Used to display doctor call information and multimedia guidance information. It is a professional LCD display with network playback capabilities, embedded with a network media playback terminal, designed for full automatic timed power on/off, and available in various sizes and styles for installation in different areas of the hospital and industrial applications.
- Media Playback Terminal: When there are existing LCD TVs in the hospital, the system can provide an independent network media playback terminal that receives data and signals from the network to display the content that needs to be played in real-time.
Data Layer:Used for the collection and aggregation of data registration and queue call information.
Application Layer:Organizes and controls the scheduling of data and content, and accepts interactive trigger events from doctors and nurses to generate information display lists.
Presentation Layer:Parses the received data and generates display data through network terminals.
1, Hospital Lobby: The outpatient lobby of the hospital is the most crowded place, where patients and accompanying persons generally need to be diverted to various departments and wards. People here need guidance the most, allowing patients and accompanying persons to easily obtain medical process information, hospital electronic maps, specialty outpatient and department introductions, authoritative doctor and expert information, etc., thereby quickly diverting crowds, improving hospital work efficiency, and allowing patients to receive treatment as soon as possible, reducing their suffering.
2, Waiting Area:Promoting new drugs, therapies, and new medical instruments in the specialty outpatient area, making it convenient for patients to understand medical dynamics and improving the hospital's economic benefits.
3, Elevator Area:Common passageways like elevators can play hospital images, product advertisements, etc., through video terminals while customers wait and rest, making it convenient for patients to understand and trust the hospital, psychologically assisting doctors in treating patients, while also shaping the hospital's brand image. It can also broadcast public information such as weather information, cold indices, clocks, etc., improving viewing effects, increasing advertising revenue, and further enriching broadcast content.
4, Patient Activity Area: Through our company's digital media publishing system, the hospital can broadcast the treatment and rehabilitation measures accumulated over the years to patients through closed-circuit television, allowing patients to understand the precautions during their recovery, along with doctors' medical advice, further deepening patients' impressions. Using this channel, the hospital can also release various prevention and treatment measures for epidemics, infectious diseases, and common diseases to patients; play relaxing programs such as music, scenery, and drama sketches that can alleviate patients' pain. Providing a set of mental relaxation information programs for hospitalized patients to improve treatment effects.
5, Conference Room:Through our company's publishing system, remote centralized training for hospital staff can be conducted, allowing for business or other learning anytime and anywhere.
6, Other Functional Areas:Connected with other internal systems of the hospital and interfacing with the hospital registration system, patients can see their order, facilitating certain special patients, while also alleviating the anxiety of patients and their families during waiting, and improving the overall external image of the hospital.
Significance
1.Serve patients and reflect humanistic care. By building an effective information platform, provide services for patients at different stages, including pre-consultation, in-consultation assistance, and post-consultation follow-up care.
2.Serve doctors and provide auxiliary diagnosis. This information platform inputs rich medical information and integrates expert experience to form a system. This system prompts doctors to make more judgments during the diagnosis process, which can greatly reduce medical accidents and is expected to improve the current situation where doctors mainly rely on experience for diagnosis.
3.Serve hospital managers and improve management efficiency. This system can determine the time spent in each link and the time consumed at each stage. Such detailed monitoring management can greatly improve the work efficiency of the hospital.
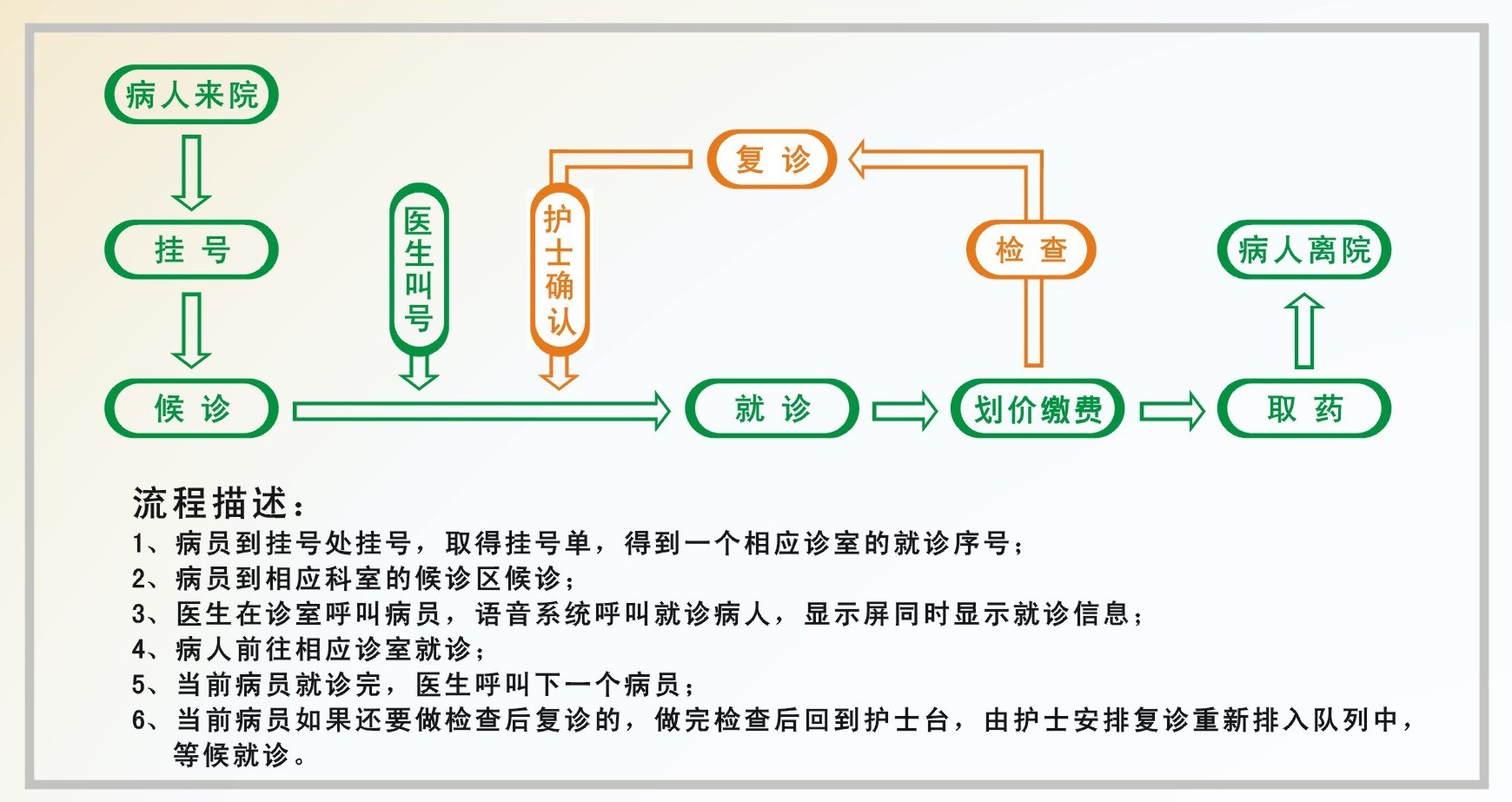
In the traditional medical treatment model, patients need to queue repeatedly for registration, payment, and obtaining examination reports during a single medical visit. However, by using the outpatient self-service, patients holding a medical treatment card can easily complete the processes of registration, payment, inquiry, and printing reports at the self-service machine after pre-charging their hospital medical treatment card, thus avoiding the hassle of repeated queuing.
First-time patients can handle medical treatment card applications and recharge services at the patient service center. If the prepaid account balance is insufficient, patients can also recharge their medical treatment card at the recharge window and then proceed with examinations after settlement. All registration, payment, prescription, and hospitalization payment services are conducted through the medical treatment card. Any unused amount from this visit can be refunded at the window or carried over for use during the next hospitalization.
After completing the card processing, registration can be divided into two parts for diversion:
- For patients who have already identified the required consultation room (doctor), they can select the department or specialist at the registration window (or self-service registration machine) in the outpatient hall. By swiping their medical treatment card, the required medical services such as registration and payment will appear on the screen. After confirming that everything is correct, the relevant fees will be automatically deducted from the prepaid account. At this point, the patient's registration information is promptly pushed to the queue calling screen next to the relevant consultation room, and the patient's consultation sequence is already in queue, waiting for the consultation.
- If the patient has not specified a particular doctor, they can choose a general number or a specialist number at the registration window (or self-service registration machine). After completing registration (payment), they can directly find the required consultation room. After confirming the consultation in that room, they swipe their medical treatment card at the queue calling screen next to the consultation room, and the patient's waiting sequence for consultation begins in that room, with the patient waiting in the consultation room's waiting area.
After the doctor issues a prescription, the patient can directly go to the medical technology department to swipe their card for payment and examination. After the examination is completed, they can promptly print the examination results using the self-service report machine, saving the time of queuing for payment and report collection.
1The triage queue management system can connect with the registration system through software interfaces, obtaining patient registration information such as name, consultation sequence number, medical record number, department, etc., in real-time from the registration system, avoiding duplicate entry, and printing a triage number on the registration slip as the consultation calling number, making full use of the existing HIS system.
2Based on the distribution of departments on each floor, we design a triage desk for each department to manage the triage queue for all departments on that floor; the number of nurse triage registrations, virtual calling terminals, comprehensive display screens for calling information, calling room display screens, and speakers will be configured according to the waiting area situation, displaying calling information for patients in that waiting area. Multiple waiting areas for the same department will display the same calling information.
3Since most departments' waiting areas are adjacent, to prevent the calling information from different departments from interfering with each other and causing patients to enter the wrong consultation room, we recommend configuring a 42-inch LCD all-in-one machine for the information display screen, showing the department calling the patient, patient number, name, and consultation room number to clearly prompt the patient; the information display screen is illustrated as follows:
4An open interface is reserved to integrate and expand with the hospital's HIS and PACS systems.